The prostate is a small gland found in men’s bodies. It plays an important role in the reproductive system. However, as our age, the prostate can grow larger. While some growth is normal, too much can cause problems. But how big is too big? Let’s understand when prostate size becomes dangerous and what you should do about it.
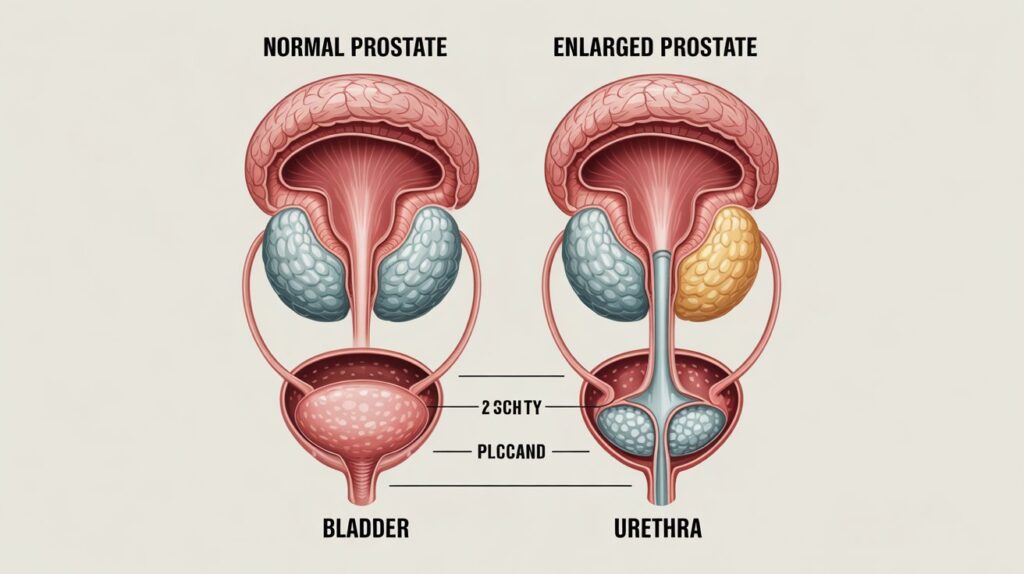
Table of Contents
What Is the Prostate and What Does It Do?
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland located below the bladder. It surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body. The main job of the prostate is to produce a special fluid that helps sperm move during reproduction.
A healthy prostate usually measures around 20 to 30 milliliters (ml) in volume or about 3 cm long and 4 cm wide. However, as men grow older, the prostate naturally gets bigger.
Why Does the Prostate Grow?
The prostate grows due to hormonal changes. As our age, their bodies produce less testosterone and more of a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This hormone makes the prostate increase in size. This condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which means non-cancerous prostate enlargement.
Prostate growth is common after age 40, and by age 60, more than 50% of men have some level of BPH.
What Prostate Size Is Considered Dangerous?
A normal prostate is about 20-30 ml in volume. When it grows larger than 40 ml, it may start causing symptoms. If the prostate grows beyond 80-100 ml, it can lead to serious problems like difficulty urinating, bladder damage, or kidney issues.
Here’s a general guide to prostate size and risk levels:
| Prostate Size | Risk Level | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| 20-30 ml (Normal) | No risk | No symptoms |
| 30-40 ml | Mild risk | Occasional urination issues |
| 40-80 ml | Moderate risk | Frequent urination, weak urine flow |
| 80-100+ ml | High risk | Pain, blocked urine flow, kidney damage |
If the prostate reaches 100 ml or more, it is considered dangerous and needs immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate
A growing prostate can press on the urethra and bladder, leading to problems. Some common symptoms include:
✔️ Frequent urination – Especially at night
✔️ Weak urine stream – Takes longer to empty the bladder
✔️ Difficulty starting urination – Feeling the need to push
✔️ Dribbling at the end of urination – Not emptying completely
✔️ Pain while urinating – May indicate infection
✔️ Blood in urine – A serious warning sign
✔️ Feeling of incomplete emptying – Even after urinating
If you notice these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
Dangers of a Large Prostate
A very large prostate can lead to serious health problems:
🚨 Urinary Retention – Complete blockage of urine flow, needing emergency treatment.
🚨 Bladder Damage – Over time, the bladder muscles weaken and cannot push out urine properly.
🚨 Kidney Damage – Blocked urine flow can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
🚨 Infections – Bacteria can grow in leftover urine, causing painful infections.
Ignoring prostate problems can make things worse, so early treatment is important.
How Is Prostate Size Measured?
Doctors use different tests to check the size of the prostate:
🔹 Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): The doctor feels the prostate through the rectum.
🔹 Ultrasound: A scan that shows the prostate’s size and shape.
🔹 PSA Test: A blood test that checks for prostate-specific antigen, which can indicate problems.
🔹 MRI or CT Scan: Advanced imaging for detailed results.
If you have symptoms, your doctor may recommend one of these tests to check your prostate size.
How to Prevent Prostate Enlargement
While aging is natural, you can take steps to keep your prostate healthy:
🥦 Eat a Healthy Diet – Foods rich in vitamins and antioxidants help. Include:
- Tomatoes 🍅 (rich in lycopene)
- Green vegetables 🥦 (fiber for digestion)
- Nuts and seeds 🥜 (healthy fats for hormones)
🏃 Stay Active – Regular exercise improves circulation and reduces risk.
💧 Drink Enough Water – Helps flush out toxins and supports bladder health.
🧘 Reduce Stress – Too much stress can affect hormone levels and prostate health.
🚫 Avoid Too Much Alcohol & Caffeine – They can irritate the bladder.
A healthy lifestyle can help prevent severe prostate enlargement.
Treatment Options for Enlarged Prostate
If your prostate is too large and causing problems, doctors may recommend:
1. Medications
Certain medicines can shrink the prostate or relax muscles to improve urination.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Changing diet, reducing stress, and regular exercise can help manage symptoms.
3. Surgery (For Severe Cases)
If the prostate is over 80-100 ml, surgery may be needed. Common surgeries include:
🔹 TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate) – Removes extra prostate tissue.
🔹 Laser Therapy – Uses laser energy to shrink the prostate.
🔹 Prostatectomy – Full removal of the prostate (for extreme cases).
Surgery is usually a last option when symptoms are severe.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience any of these symptoms, visit a doctor:
❗ Frequent nighttime urination
❗ Difficulty urinating or pain
❗ Blood in urine
❗ Feeling that the bladder isn’t empty
❗ Sudden inability to urinate
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications.
Conclusion
The prostate is a small but important gland in a man’s body. A normal prostate size is 20-30 ml, and if it grows beyond 40 ml, it may cause symptoms. If it reaches 80-100 ml or more, it can become dangerous and require treatment.
By eating healthy, staying active, and visiting a doctor for regular checkups, men can maintain a healthy prostate and avoid serious health issues. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, don’t ignore them—get medical help early!
💬 Have questions about prostate health? Drop them in the comments below!


